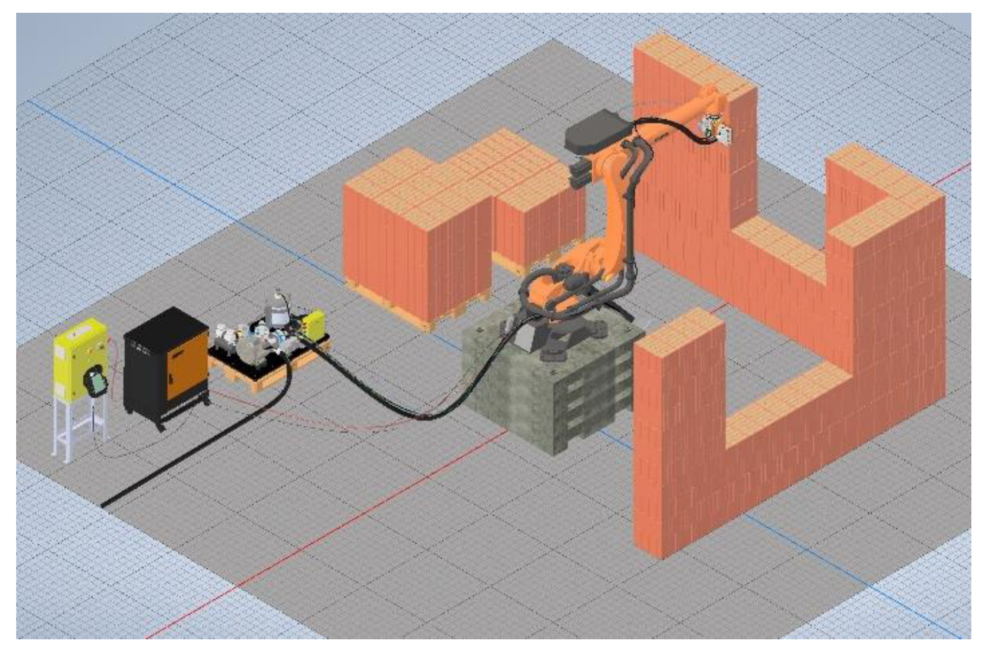
Building with robots just got a whole lot more modular, thanks to a new system that uses lattice blocks and autonomous construction bots. This technology has the potential to revolutionize construction on Earth and beyond, from building shelters on Mars to erecting disaster relief structures in remote areas.
Key Highlights:
- Modular lattice blocks: Specially designed, interlocking blocks form the building blocks of the system.
- Autonomous robots: Three robots work together, transporting, manipulating, and connecting the blocks.
- Construction on-demand: Robots can build structures based on pre-programmed plans or adapt to changing needs.
- Versatility: Suitable for various applications, from shelters and bridges to disaster relief and off-world construction.

A New Era of Building Blocks:
Imagine a construction site where robots, not humans, lay the bricks. This is the future envisioned by a team of engineers from NASA Ames Research Center and KBR, who have developed a robotic system that autonomously builds structures using specially designed lattice blocks.
These blocks, resembling hollow coat hangers, interlock seamlessly, allowing robots to connect them without needing specialized tools or human intervention. The system comprises three robots: two for transporting blocks and one for connecting them. Each robot can latch onto any block, enabling efficient material handling and construction.
Building Beyond the Horizon:
The potential applications of this technology are vast. NASA is particularly interested in its use for constructing shelters on Mars or other planets. The robots could autonomously deploy pre-fabricated structures, providing essential living quarters for astronauts without the need for human construction crews.
On Earth, the system could be used for rapid construction in disaster zones, where deploying robots into dangerous or remote areas could save lives. Additionally, the modular nature of the lattice blocks makes them ideal for building bridges, temporary shelters, and other structures that need to be adaptable and easy to disassemble.
Challenges and the Road Ahead:
While the technology is promising, there are still challenges to overcome. One key hurdle is ensuring the robots can operate reliably in harsh environments, such as the Martian surface. Additionally, the system currently relies on pre-programmed construction plans. Developing algorithms for real-time adaptation to changing circumstances will be crucial for wider deployment.
Despite these challenges, the potential of robots building with lattice blocks is undeniable. This technology has the potential to transform the construction industry, making it faster, more efficient, and safer, both on Earth and in the cosmos.
How the robots work:
The robots use a combination of sensors and cameras to navigate around the construction site and identify the location of the lattice blocks. They then use their manipulators to pick up the blocks and move them to the desired location. Once the blocks are in place, the robots use a special tool to connect them together.
Benefits of using lattice blocks:
Lattice blocks are a type of modular building block that is easy to assemble and disassemble. They are also very strong and can be used to build a variety of structures, from simple shelters to complex buildings.
Challenges of using robots for construction:
One of the biggest challenges of using robots for construction is that they can be expensive to develop and maintain. Additionally, robots can be difficult to program and may not be able to adapt to changes in the construction site.
The Future of Construction:
The robotic construction system with lattice blocks is a glimpse into the future of building. As the technology matures and becomes more affordable, we can expect to see robots playing an increasingly important role in construction projects of all shapes and sizes. This not only promises to revolutionize the industry but also opens up exciting possibilities for building in remote and challenging environments, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible on our own planet and beyond.