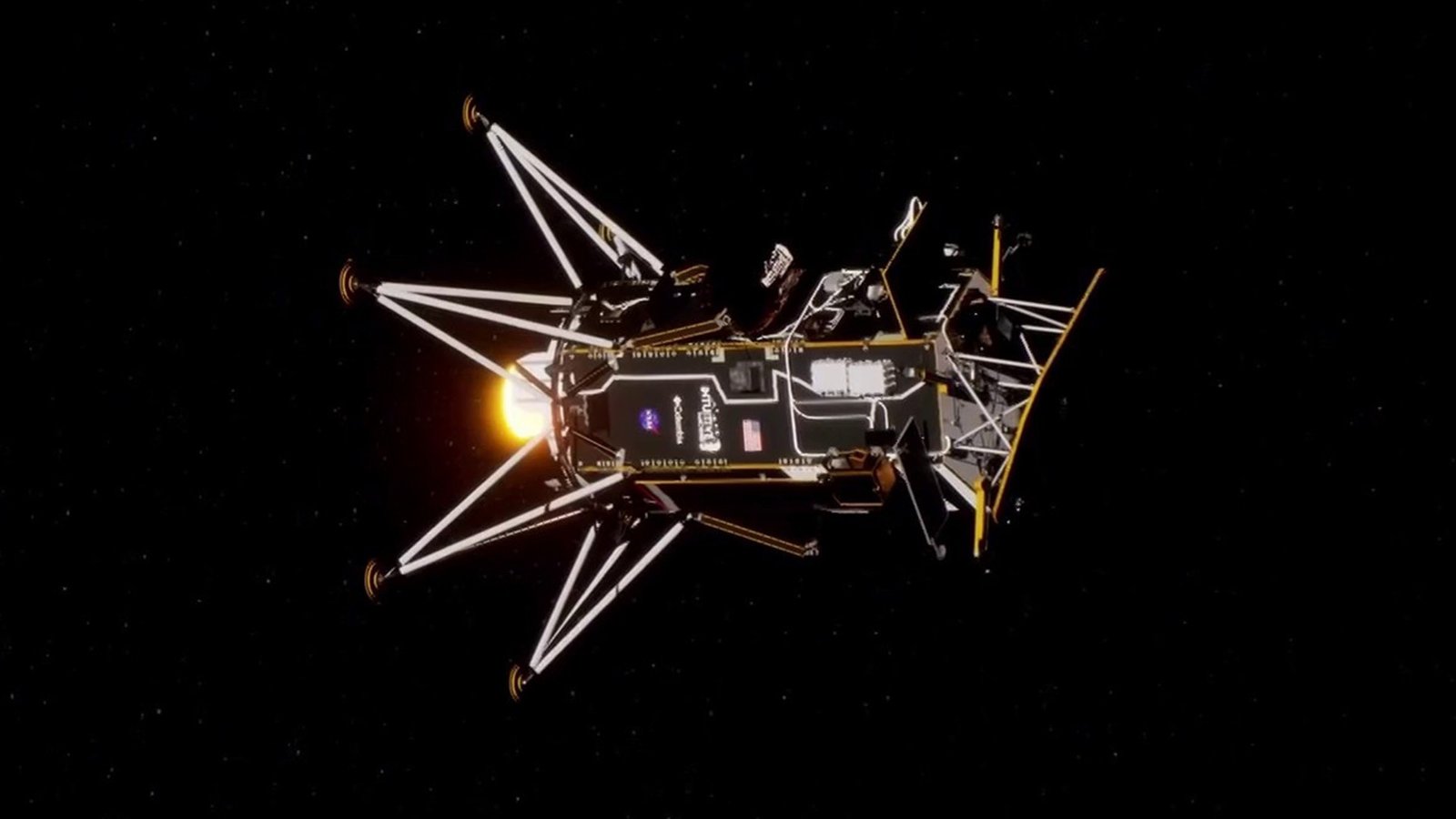
Intuitive Machines, a Houston-based commercial space company, is making history this week as its Odysseus lunar lander attempts to become the first American commercial spacecraft to make a soft landing on the moon. The mission, known as IM-1, marks an important step in NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative, aiming to partner with private firms for future lunar deliveries.
Key Highlights
- Mission objective: Test technology and deliver science payloads to the lunar surface
- Launch date: The Odysseus lander launched in early 2024
- Possible landing date: Intuitive Machines is targeting a landing attempt as early as February 22nd, 2024.
- Landing site: Malapert A crater, near the lunar south pole.
- Significance: A successful landing would make Intuitive Machines the first private company to land on the moon.
Critical Stages of the Mission
The IM-1 mission has already gone through several significant phases:
- Launch: The Odysseus lander launched from Earth aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket.
- Lunar Orbit Insertion: The lander successfully entered lunar orbit.
- Descent Preparations: Odysseus is currently preparing for the powered descent phase, a delicate maneuver involving controlled firing of the spacecraft’s engines to slow its fall towards the moon’s surface.
Technical Details
- Lander Design: Delve into the specifics of the NOVA-C lander. Describe its size, shape, propulsion system, and any unique features aiding in the landing attempt.
- Navigation Technology: Explain how Odysseus is using Terrain Relative Navigation (TRN) to navigate the moon’s surface and identify a safe landing spot.
Payload Details
- Specific Instruments: List the names and purposes of the NASA payloads, including the instruments designed to study space weather and lunar resources.
- Commercial Payload Descriptions: Provide short summaries of the goals of the commercial payloads on board. These could include potential technology demonstrations, cameras designed for outreach, or artistic payloads.
History and Context
- Previous Attempts: Briefly mention previous successes and failures in commercial moon landing attempts (there have been a few). This highlights the challenges Intuitive Machines faces.
- The Artemis Program: Explain how the IM-1 mission and CLPS initiative fit into the broader goals of NASA’s Artemis program, aiming to return humans to the moon. Discuss how this private mission is a stepping stone towards greater goals.
The Landing Challenge
Achieving a successful soft landing on the moon is notoriously challenging. The spacecraft must autonomously navigate the complexities of the lunar surface and manage its descent. The targeted landing site of Malapert A, along the rim of a crater, provides valuable scientific opportunities but also poses potential complications during landing.
What’s on Board?
The Odysseus lander carries a range of important payloads for NASA:
- NASA-provided payloads: Instruments to study lunar space weather conditions and to measure potential resources
- Commercial payloads: A variety of payloads including technology demonstrations and cameras.
The Future of Lunar Exploration
The success of the Odysseus mission could usher in a new era of commercial lunar exploration. NASA’s Artemis program aims to establish a long-term human presence on the moon. Commercial partnerships like the CLPS initiative are considered key to achieving this ambitious goal. If Intuitive Machines is successful, it will create more opportunities for private companies to play significant roles in future space missions and the development of a lunar economy.
The potential touchdown of the Odysseus lunar lander is a defining moment for the commercial space sector. This bold endeavor demonstrates the growing capabilities of private companies and their potential to be major players in lunar exploration. The world watches with anticipation as this historic moon landing attempt plays out.