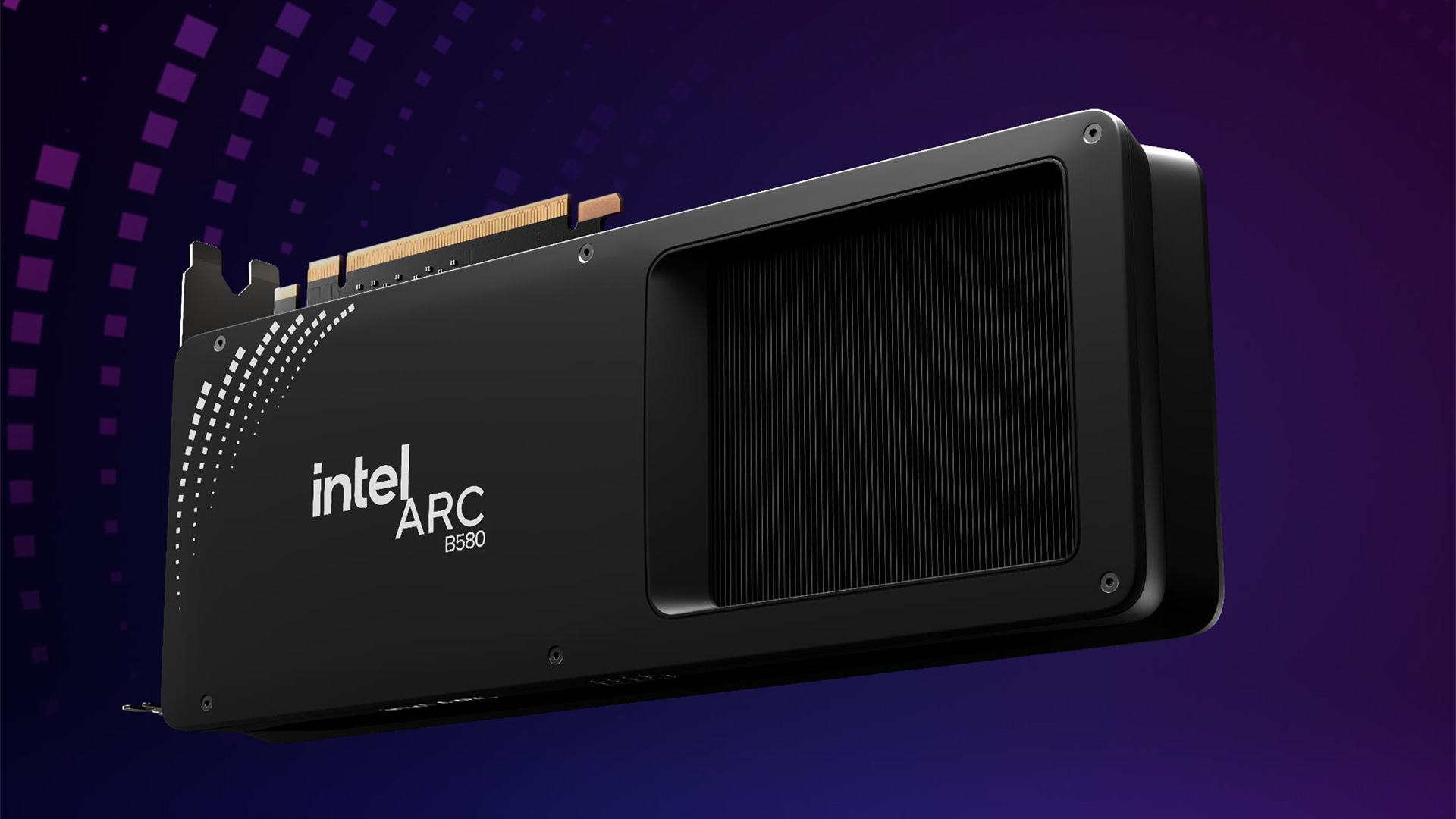
ONIX Technology, a fresh face in the graphics card arena, has emerged from relative obscurity to announce its inaugural lineup of GPUs based on Intel’s Arc B580 Battlemage architecture. While the company itself remains somewhat enigmatic, with a strong focus on the Chinese market and a notable absence from global social media platforms, its website and recent press releases shed light on its origins and ambitions.
A New Contender with Experienced Roots
Though ONIX has yet to officially disclose its parent organization, reports suggest a close relationship with JWIPC, a company renowned for its Intel-based Mini-PCs and motherboards. This connection hints at a potential expansion of JWIPC’s expertise into the dedicated graphics card sector, leveraging the company’s reported 420-strong research and development team and nine years of industry experience.
ONIX’s website outlines three distinct product series: ONIX ATLAS, ONIX LUMI, and ONIX Odyssey. Of these, the LUMI and Odyssey series have taken center stage with the unveiling of their respective Arc B580 and Arc B570 models.
LUMI and Odyssey: A Tale of Two Series
The LUMI series distinguishes itself with a striking white aesthetic and integrated RGB lighting, catering to users seeking a visually distinctive build. Furthermore, the LUMI series features a factory-overclocked Arc B580 model boasting a 203W Total Board Power (TBP), a notable increase over Intel’s official specifications. This suggests a focus on performance, potentially targeting enthusiasts and gamers seeking higher clock speeds.
In contrast, the Odyssey series appears to adopt a more understated design, with both Arc B580 and Arc B570 models sharing a similar physical appearance and dimensions with their LUMI counterparts. This series may appeal to users prioritizing functionality and value over aesthetics.
PCIe 5.0 x8: A Potential Discrepancy
One of the more intriguing claims made by ONIX is the inclusion of PCIe 5.0 x8 support for its graphics cards. This assertion contradicts Intel’s official confirmation of PCIe 4.0 support for the Arc B580. While it is technically plausible for the Arc B580 GPU to accommodate the newer PCIe standard, it remains to be seen whether ONIX has implemented this feature in its cards. This discrepancy could stem from preliminary information shared by Intel with its partners or simply be an oversight on ONIX’s part.
Pricing and Availability in the Chinese Market
ONIX has announced that the B580 LUMI OC model will be available for purchase starting December 13th, priced at 2,199 RMB. The company is also offering a three-year warranty on its products, providing consumers with added peace of mind. However, specific retail partners for ONIX graphics cards have yet to be disclosed.
With its entry into the graphics card market, ONIX brings a new dimension to the competitive landscape, particularly within the Chinese market. The company’s close ties to JWIPC, coupled with its focus on distinct product series and competitive pricing, position it as a potential contender in the burgeoning Arc Battlemage ecosystem.