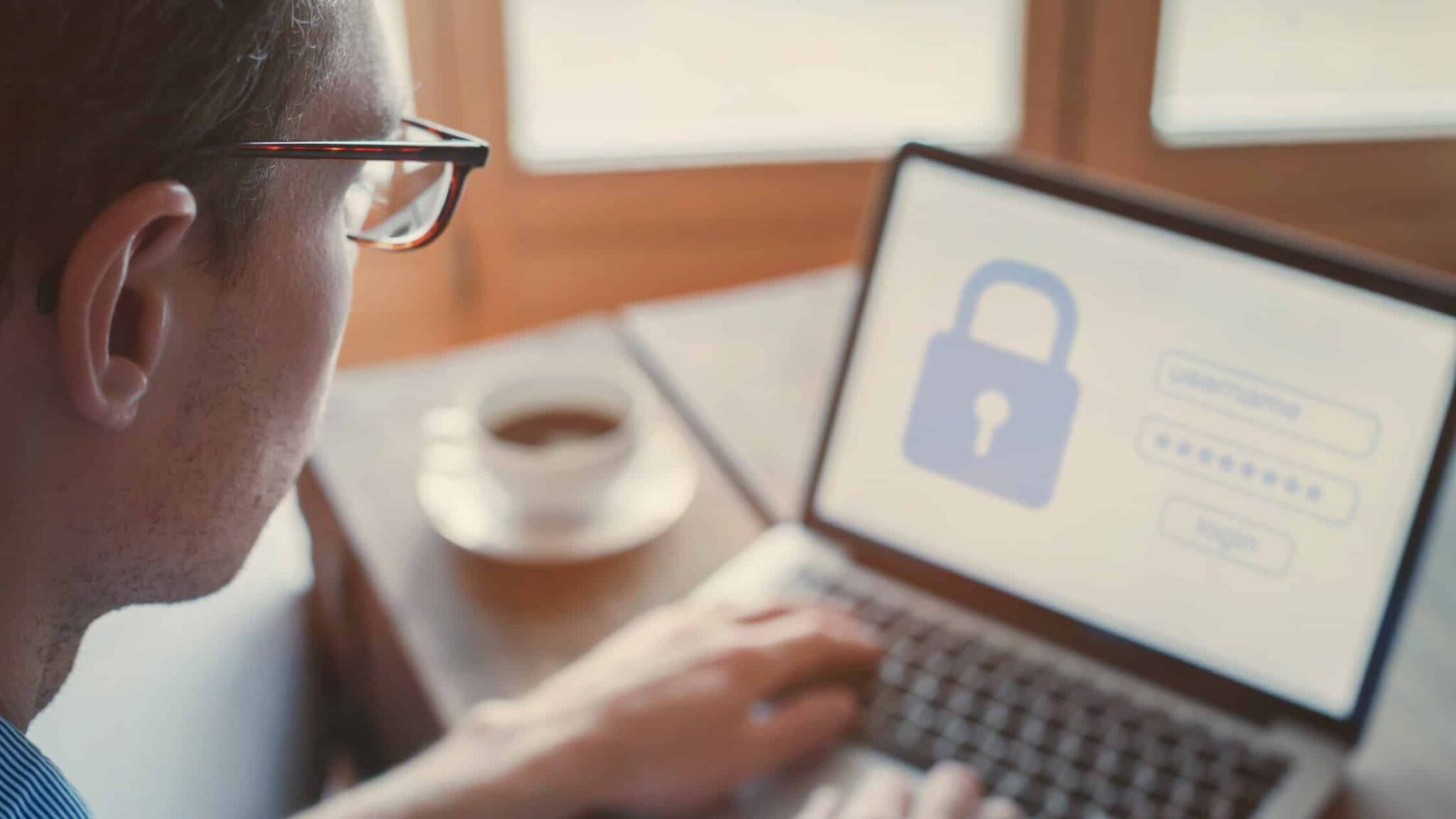
As remote work becomes increasingly prevalent, protecting company data has become more challenging. Here are nine effective strategies to enhance data security for employees working remotely.
Provide Company-Owned Devices
Supplying employees with company laptops and phones allows for complete management and security control over the devices accessing sensitive data. It’s advisable to ensure all devices are updated and encrypted with SSL certificates. If providing devices isn’t feasible, employers should at least offer resources for employees to secure their own equipment, such as company-provided anti-malware software.
Conduct Application Scans and Penetration Tests
Regular penetration testing simulates cyberattacks to identify system vulnerabilities before hackers can exploit them. It’s crucial to guard against privilege escalation attacks, where an intruder gains unauthorized access and elevates their privileges to access sensitive information. Strengthening defenses in this area limits critical application access even if an employee’s credentials are compromised.
Implement Company-Wide VPN Usage
With data breaches costing businesses an average of $4.45 million in 2023, investing in tools that mitigate vulnerabilities is essential. Encouraging all employees to use virtual private networks (VPNs) protects data that might otherwise be exposed on unsecured home or public networks. VPNs are easy to implement and offer an additional layer of security.
Deploy a Web Application Firewall
In addition to VPNs, utilizing a Web Application Firewall (WAF) helps protect web applications from attacks. Employers should consider AI/ML-based WAFs that detect anomalies and block illegitimate requests, even if they come through compromised employee credentials.
Use Encryption Software
Encryption software adds a layer of protection by making stolen files inaccessible to unauthorized users. Employers should establish security policies that educate workers on how and when to encrypt files. Regular checks can ensure compliance with these practices.
Enforce Strict Password Management
Strong password management is vital in reducing the risk of data breaches. This includes using automatic password generators to create secure, unique passwords and avoiding the reuse of passwords across multiple accounts. For accessing sensitive data, implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring multiple forms of identity verification.
Apply Rigorous Access Controls
Limiting access to sensitive data minimizes security risks. Employers should adhere to the principle of least privilege, granting users access only to the specific resources necessary for their roles. Removing files when they are no longer needed and promptly revoking access when it’s no longer required are also important practices.
Equip Employees with Necessary Tools
A significant risk of remote work is employees resorting to unsanctioned tools or practices to facilitate their tasks, such as using unsecured apps or channels. To prevent this, provide remote workers with all the approved tools they need and make them aware of the platforms available to them. Security policies should mandate the approval of web app purchases and downloads to mitigate risks associated with open-source and cloud-based applications.
Offer Comprehensive Training to Remote Workers
Security measures are ineffective if employees are unaware of procedures and their importance. In 2023, over 352 million individuals were affected by data compromises, underscoring the need for organizations to train employees on identifying sensitive data and protecting it. Training can be engaging, such as using phishing email simulators to demonstrate potential threats. Regular education ensures remote workers are prepared to keep company data secure.
Venky Sundar, Founder and President of Indusface, highlights the data security challenges of increased remote work:
“Remote working means people are operating in less secure environments, making devices more susceptible to data breaches both digitally and physically. Many are using the same device for professional and personal use or even sharing devices with household members.
“Employers can no longer rely on security strategies designed for in-office work; data is no longer confined under one roof where IT can supervise. It is crucial that employers adapt to this new way of working and protect themselves from vulnerabilities. Defenses such as firewalls, penetration testing, and VPNs are more critical than ever.”